What is Lymphedema?
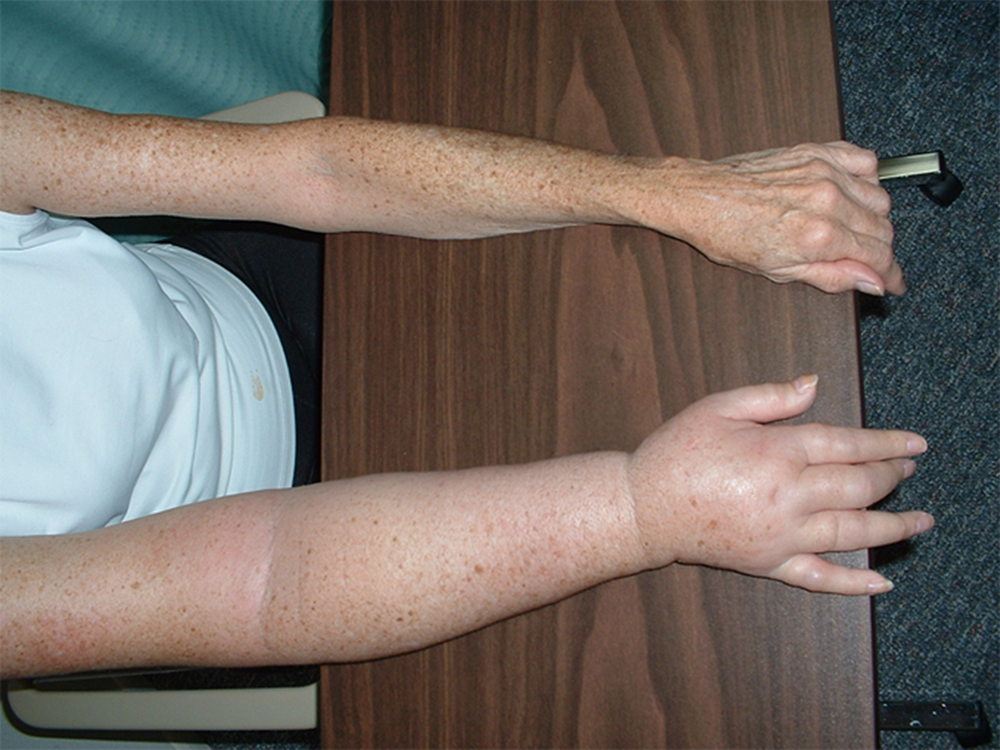
Lymphedema is fluid retention in tissues that presents as swelling of a body part. According to the International Society of Lymphology Consensus Document (Lymphology, 2016), an accurate diagnosis of lymphedema is only made when edema results from an impairment of the lymphatic system causing a reduced transport capacity. Edema can also occur in an intact lymphatic system that is overwhelmed by an increased fluid load.
The most common etiology of lymphedema worldwide is filariasis, a parasitic infection that damages the lymphatics and is primarily limited to tropical and subtropical regions. Poor access to health care, limited education regarding transmission prevention, improper hygiene and skin care contribute to increased incidence. In the United States, however, more common reasons for the development of lymphedema are surgery, especially for cancer when lymph nodes are removed, radiation treatments, and congenital malformation of the lymphatics. These all can result in a disruption of lymphatic drainage that leads to swelling in the affected body region.
Conventional Treatment of Lymphedema
Conservative treatment of lymphedema has evolved to consist of:
- manual lymph drainage (a gentle massage technique that reroutes fluid around obstructions)
- compression bandaging
- decongestive exercises
- meticulous skin care and
- compression garments.
Other modalities which may be employed to augment management of lymphedema can include microsurgery and the use of pneumatic compression pumps. Recently, people with lymphedema as well as clinicians and researchers are investigating the importance of nutrition in improving lymphedema treatment outcomes.
Evidence for Ketogenic Therapy for Lymphedema
In particular, in my practice, I have seen that helping patients implement a ketogenic diet along with conventional therapy results in astounding improvements in the health and life satisfaction.
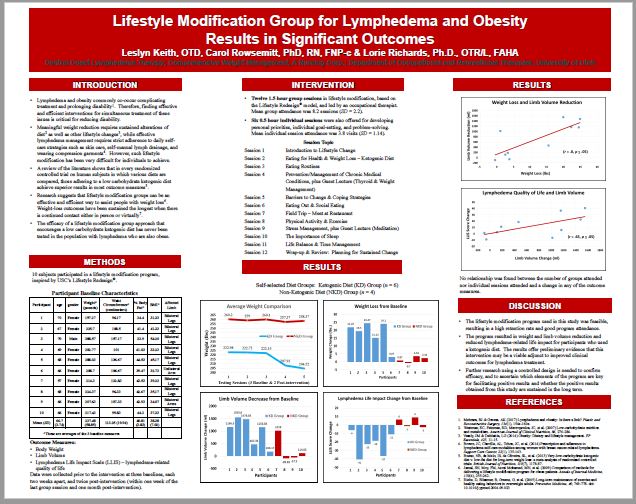
In 2017, my colleagues and I undertook a small trial in which the use of a ketogenic diet to treat lymphedema was studied. The patients involved in the study experienced improvements across many outcome measurements. The final results were published in the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine in November 2017, and I gave an poster presentation of the results at the Obesity Medicine Association conference in San Antonio, TX in September of 2017.
For More Resources:
Keto and Fasting for Lymphedema Facebook Group
Other Suggested Reading
Lymphedema Management by Joachim Zuther
Földi's Textbook of Lymphology by Michael and Etelka Földi
(Please Note: As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.)
Books by Leslyn Keith, OT
|
Buy the print softcover book on Amazon Buy the E-book via Paypal |
Buy the print softcover book on Amazon Buy the E-book via Paypal |
Follow Leslyn Keith on YouTube!
Done with Lymphedema, back to Home.